
The Sanderson Group Webpages
Department of Chemistry
Durham University, Durham, UK
Membrane Proteins
We are examining some of the factors that control the activity of membrane proteins. Our research focuses on two areas:
- proteins with unusual lipidation profiles; and
- matrix proteins from enveloped viruses.
Our particular interests lie in understanding how chemical processes influence to the long term stability of proteins in the membrane.
Aquaporin-0
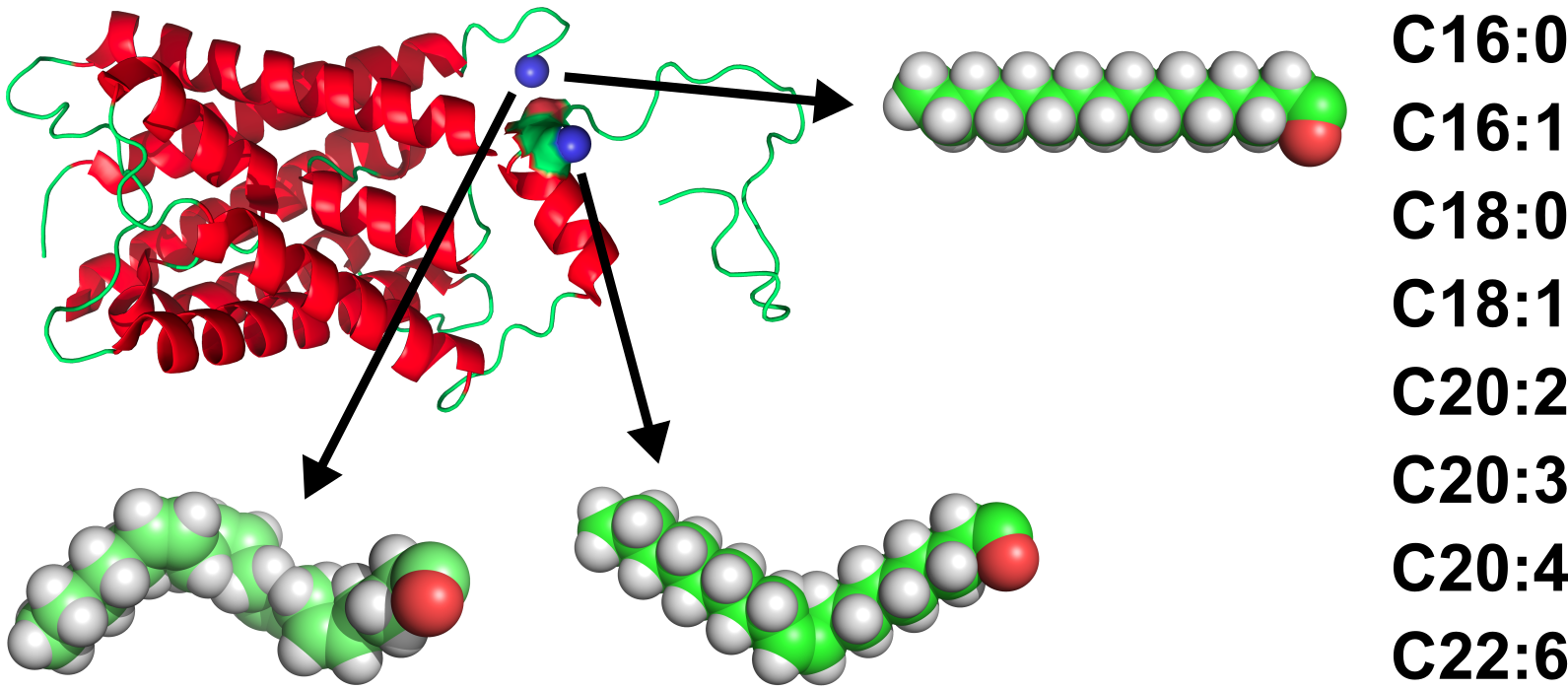
In collaboration with Prof. Roy Quinlan and Dr Jackie Mosely, we examined the post-translational modifications that occur to the lens protein aquaporin-0 (AQP0). We have established that two positions on the protein, the N-terminal amino group and the side chain amino group of Lys238, are modified with a series of acyl chains, including in decreasing order of abundance: oleoyl, palmitoyl, stearoyl, eicosenoyl, dihomo-γ-linolenoyl, palmitoleoyl and eicosadienoyl. The relative abundances of these modifications mirror the fatty acid composition of lens phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) lipids.1
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) M Protein
We have examined the structure and membrane activity of the RSV matrix (M) protein and solved its crystal structure.2 The interfacial behaviour of the protein is dependent on the lipid composition of the membrane.3 (more)
References
- "The lipidation profile of aquaporin-0 correlates with the acyl composition of phosphoethanolamine lipids in lens membranes", Vian S. Ismail, Jackie A. Mosely, Antal Tapodi, Roy A. Quinlan and John M. Sanderson, Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Biomembr., 2016, 1858, 2763–2768. (green open access version)
- "Influence of Lipids on the Interfacial Disposition of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein", Helen K. McPhee, Jennifer L. Carlisle, Andrew Beeby, Victoria A. Money, Scott M. D. Watson, Robert P. Yeo and John M. Sanderson, Langmuir, 2011, 27, 304-311.
- "Surface Features of a Mononegavirales Matrix Protein Indicate Sites of Membrane Interaction", Victoria A. Money, Helen K. McPhee, Jackie A. Mosely, John M. Sanderson and Robert P. Yeo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2009, 106, 4441-4446.